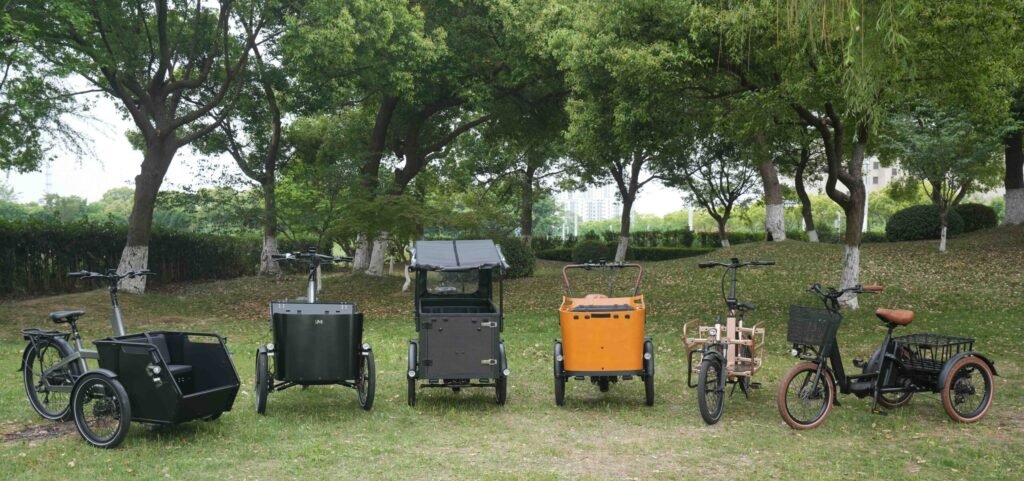
Cargo e-bikes are shaping the future of sustainable transport, combining practicality with efficiency for both businesses and families. This guide covers the main cargo e-bike types, essential components, motor systems, EU regulations, and market insights—providing a clear industry reference for B2B decision-makers.
Types of Cargo E-Bikes
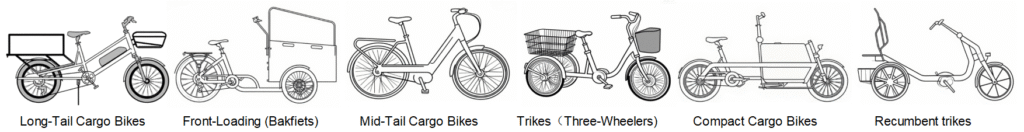
Cargo e-bike types vary widely, designed to meet the needs of families, commuters, and businesses handling deliveries or bulk transport.
Long-Tail Cargo Bikes
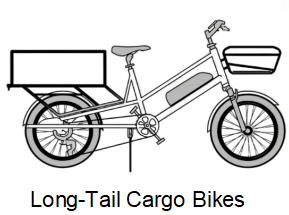
One of the most popular cargo e-bike types, long-tail cargo bikes extend the rear frame to carry extra passengers or goods.
- Capacity: 40–100kg
- Passengers: One to three children on the rear deck
- Advantages: Easier handling due to standard bike feel, convenient storage
- Use Cases: Family school runs, light deliveries, grocery shopping
- Examples: Specialized Globe Haul, Trek Fetch+
More reading about Long tail Cargo E-Bike which Gain Momentum Across Europe
Front-Loading Cargo Bikes (Bakfiets)

Front-loading cargo bikes, often called bakfiets, feature a large box in front for maximum visibility.
- Capacity: 80–150kg
- Passengers: Two to four children
- Advantages: Rider can monitor children or goods, optional weather covers
- Use Cases: Commercial deliveries, mobile coffee stands, family rides
- Variants: Agile two-wheelers or stable three-wheelers
Mid-Tail Cargo Bikes(similar as city e-bike)
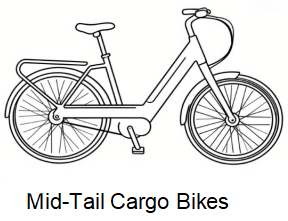
A more compact take on long-tail designs, these are a versatile cargo e-bike type suitable for urban riders.
- Capacity: 30–60kg
- Passengers: One to two children
- Advantages: Easy to park, highly manoeuvrable
- Use Cases: City commuting with modest loads
Cargo Trikes (Three-Wheelers)
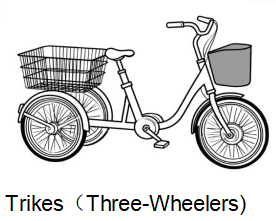
For businesses handling heavier logistics, cargo trikes offer unmatched stability.
- Capacity: 100–200kg+
- Advantages: Stable when stationary, accessible for older riders
- Disadvantages: Wider design, different handling
- Use Cases: Large-scale delivery, mobility for elderly or disabled users
Compact Cargo Bikes
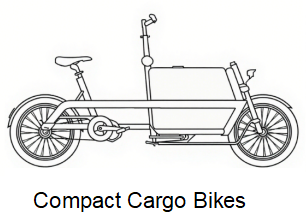
Compact designs balance practicality with portability, ideal for inner-city users.
- Capacity: 20–40kg
- Advantages: Lightweight, easy storage, cost-effective
- Use Cases: Small deliveries, commuting, groceries
Recumbent Cargo Bikes
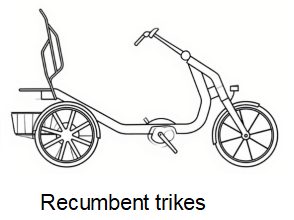
Recumbent cargo bikes combine the ergonomic benefits of recumbent cycling with practical cargo-hauling capabilities.
- Examples: Hase Pino Cargo, Azub Recumbent Cargo Trike.Essential Components
- Description: Rider sits in a reclined position with pedals at the front, cargo area usually positioned behind or beneath the seat.
- Capacity: 40–120kg cargo weight depending on design.
- Passengers: Typically 1–2 children in rear or side-mounted seats.
- Advantages: Superior comfort for long rides, reduced strain on rider’s back and wrists, aerodynamic efficiency for extended commutes.
- Disadvantages: Larger footprint than upright cargo e-bikes, more challenging in stop-and-go urban traffic.
- Use Cases: Long-distance cargo commuting, sustainable touring with cargo, niche delivery applications where rider comfort is critical.
Frame & Structure
Reinforced aluminium alloy is most common, with steel and carbon fibre alternatives. Frames feature low step-throughs for accessibility and integrated mounting points for cargo solutions.
Cargo E-Bike Motor Systems: Hub vs Mid-Drive

Der cargo e-bike motor system is central to performance, especially under heavy load.
- Hub Motors:
- Front hub (250–500W) is simpler but less efficient for cargo.
- Rear hub (250–750W) offers better traction and direct drive.
- Advantage: Lower cost, easy maintenance.
- Mid-Drive Motors:
- EU limits to 250W pedal-assist, though higher power exists elsewhere.
- Brands: Bosch, Shimano, Yamaha, Brose.
- Advantage: Uses bike’s gears for efficiency, balanced weight distribution.
- Ideal for professional fleets requiring durability and performance.
Battery Technology
Modern lithium-ion batteries (400–1000Wh) power cargo e-bike motor systems, offering 40–120km per charge. Dual-battery options extend range for commercial use.
- UN 38.3: Transport testing for lithium batteries
- IEC 62133: Safety requirements for lithium cells
- Waste Directive: End-of-life battery disposal requirements
- RoHS Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances
Some essential information about E-Cargo Bike New Battery Rules.
Braking Systems
Hydraulic disc brakes with large rotors are standard, providing reliable stopping power for heavy cargo e-bike types.
Disc Brakes (Standard)
- Hydraulic: Better modulation, less maintenance, consistent performance
- Mechanical: Easier to adjust, lower cost
- Rotor Sizes: 160-203mm (larger for cargo bikes due to increased stopping power needs)
Rim Brakes (Less common on cargo bikes)
- Limited stopping power for heavy loads
- Weather-dependent performance
Drivetrain Components
Derailleur systems remain affordable, while internal hub gears and belt drives reduce maintenance for long-term fleet use.
Gearing Systems
- Derailleur Systems: 7-12 speed, traditional shifting
- Internal Hub Gears: 3-14 speed, protected from elements, low maintenance
- Automatic Transmissions: Emerging technology, optimal efficiency
Chain vs Belt Drive
- Chain: Traditional, serviceable, lower cost
- Belt: Clean, quiet, long-lasting, requires special frame design
Wheels & Tires
Cargo bikes often use mixed wheel sizes (20” front, 26” rear) with wide, puncture-resistant tyres—crucial for consistent delivery operations.
Wheel Sizes
- 20″ Front/Rear: Lower center of gravity, easier loading
- 26″ Standard: Good balance of stability and efficiency
- Mixed Sizes: 20″ front, 26″ rear for optimal handling
Tire Specifications
- Width: 1.5-2.5 inches for stability and comfort
- Puncture Protection: Essential for commercial use
- Tread Patterns: Urban, all-terrain, or specialized delivery tires
Cargo Solutions
From rear racks to front-loading boxes, cargo solutions define how a bike adapts to business needs. Options include lockable boxes for deliveries, child seats, and modular racks.
Safety & Lighting
Integrated LED lights, reflective elements, and child harnesses ensure compliance and safe operation.
Integrated Lighting
- Front Lights: LED, 50-200+ lumens
- Rear Lights: LED with brake light function
- Power Source: Bike battery or separate battery
- Regulations: Must comply with local visibility standards
Reflective Elements
- Spoke Reflectors: Side visibility
- Frame Reflectors: Integrated or adhesive
- Cargo Area Reflectors: Highlight bike dimensions
Functional Systems
Functional systems in a cargo e-bike manage power delivery, rider control, and safe load handling for commercial use.
- Assist Modes: Eco, Normal, Turbo, and Walk Assist for pushing.
- Sensors: Torque sensors ensure proportional assistance, essential for smooth performance.
- Displays: Battery life, speed, trip data, and sometimes GPS or theft protection via smartphone apps.
- Charging: Workplace charging is growing, with fast charging reducing downtime for fleets.
- Load Management: Balanced loading and secure tie-downs protect goods and passengers.
EU Regulations & Compliance
Understanding EU regulations for cargo bikes is vital for manufacturers, importers, and delivery companies.
L1e-A (Standard Cargo E-Bikes)
No Registration Required
- Maximum Continuous Power: 250W rated motor power
- Speed Assistance: Up to 25 km/h with pedal assist
- Pedal Requirement: Motor only assists when pedaling (except walk mode up to 6 km/h)
- Power Cut-off: Assistance stops at 25 km/h
No Registration Required
- Treated as conventional bicycles
- No license, insurance, or helmet requirements (though recommended)
- Access to bike lanes and paths
L1e-B (Speed Pedelecs)
Power Requirements
- Restrictions: No access to bike lanes in most EU countries
- Maximum Continuous Power: 4000W
- Speed Assistance: Up to 45 km/h
- Requirements: Registration, license plate, insurance mandatory
Safety Standards
EN 17860 sets requirements for mechanical strength, electrical safety, and stability.
More reading about EN17860 you may want know.
Manufacturing Compliance
All EU models must bear CE marking, meet UN 38.3 battery transport testing, and follow IEC 62133 for lithium battery safety.
Import/Export Rules
HS coding, customs duties (6% for complete e-bikes), and warranty compliance are key considerations for cross-border trade.
Market Considerations
Cargo e-bikes succeed commercially when tailored to specific market segments with clear ROI for businesses.
- Family Transport: €2,500–6,000, prioritising safety and weather protection
- Commercial/Delivery: €3,000–8,000, focusing on durability and low operating cost
- Pendeln in der Stadt: €2,000–5,000, offering portability and integration with public transport
Performance Metrics:
- Range of 40–80km under load
- Payloads of 40–200kg depending on design
- Regular maintenance (brakes, chains, tyres, batteries) ensures reliability
Technical Specifications
Technical specifications define whether a cargo e-bike meets industry demands for durability, safety, and efficiency.
- Performance: 0–25 km/h in 8–15 seconds; can climb 15–20% gradients fully loaded.
- Efficiency: 8–15Wh/km consumption; regenerative braking adds limited recovery.
- Sustainability: Zero direct emissions, modular upgrades extend lifespan.
- Qualitätssicherung: TÜV and SGS testing validate compliance with ISO 4210 and REACH standards.
Industry Resources
Businesses can access industry organisations and testing bodies to ensure compliance and stay competitive.
- Professional Organisations: CONEBI, LEVA-EU
- Certification Bodies: TÜV Rheinland, DEKRA, SGS
- Standards Organisations: CEN, IEC, ISO
Abschluss
From long-tail cargo bikes for families to three-wheeled trikes for logistics, cargo e-bike types are reshaping urban mobility. With the right cargo e-bike motor system, durable components, and awareness of EU regulations for cargo bikes, businesses can optimise fleets for efficiency, sustainability, and compliance.






